


Absolute value, represented as |x|, is a fundamental mathematical concept used to measure the distance between a number and zero on the number line. This distance is always positive or zero, making it a powerful tool for understanding the magnitude or size of a number, regardless of its sign. Absolute value essentially "absolutizes" a number, removing the directional aspect and focusing solely on how far it is from zero.
Absolute value is expressed using vertical bars, | |.
These bars encapsulate a numerical expression, indicating that we are interested in its magnitude rather than its sign.
For instance, |-5| equals 5, emphasizing that the magnitude of -5 is 5 units away from zero.
Absolute value has several properties that make it an invaluable tool in mathematics.
The non-negativity property states that |x| is always non-negative, ensuring that the result is either zero or positive.
The triangle inequality asserts that |x + y| is less than or equal to the sum of |x| and |y|, offering insights into inequalities.
The identity property reveals that |x| equals x when x is non-negative and -x when x is negative, reflecting the magnitude while considering the sign.
Solving absolute value equations, such as |x - 3| = 7, involves considering both the positive and negative cases.
For this equation, it means solving x - 3 = 7 and -(x - 3) = 7 separately.
The positive case yields one solution, while the negative case provides another, resulting in multiple possible answers.
x = 7 + 3 = 10
Negative Case: Solve -(x - 3) = 7.
-x + 3 = 7
-x = 7 - 3 = 4
x = -4
So, the solutions are x = 10 and x = -4.
Absolute value inequalities, like |2x + 1| < 5, require a systematic approach.
To solve them, break them into two separate inequalities: 2x + 1 < 5 and -(2x + 1) < 5.
Solve each inequality independently and combine the results to find the solution to the absolute value inequality.
Suppose you're conducting an experiment to measure the density of a substance, and the theoretical or accepted density value is 8.00 g/cm³.
After conducting your experiment, you measure the density of the substance and obtain a value of 7.60 g/cm³.
Absolute value transcends the realm of mathematics and finds practical application in various fields.
In physics, it quantifies measurement errors and distances between objects.
In finance, it tracks price changes in stocks and provides insights into market volatility.
In everyday life, it helps determine the difference between two values, making it a versatile tool for solving real-world problems.
In geometry, absolute value plays a crucial role in measuring distances between points.
It helps define geometric shapes and relationships, such as the length of sides in triangles and rectangles.
Absolute value also simplifies calculations involving coordinates, making it an essential tool in understanding the geometry of shapes.
To find the distance between these points using absolute value, we use the distance formula:
Distance (d) = |√((x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2)|
In our example:
x1 = 3, y1 = 4 (coordinates of point A)
x2 = 1, y2 = 7 (coordinates of point B)
Plugging these values into the formula:
d = |√((1 - 3)^2 + (7 - 4)^2)|
d = |√((-2)^2 + (3)^2)|
d = |√(4 + 9)|
d = |√13|
So, the distance between points A and B is √13 units, thanks to the use of absolute value in the calculation.
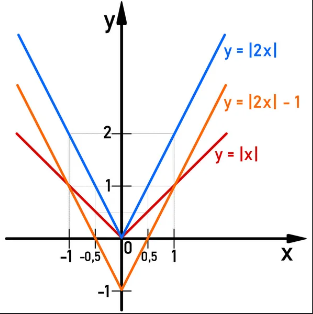
Absolute value functions are characterized by their distinctive V-shaped graphs.
These functions have a critical point called the vertex, which occurs at the absolute value expression's zero.
Understanding these functions is essential for mathematical modeling, optimization problems, and analyzing symmetric relationships in data.
Data analysts use absolute value to quantify the mean absolute deviation (MAD) of a data set.
MAD measures the average absolute difference between data points and a central value, providing valuable insights into data variability.
It's a crucial metric for assessing data quality, identifying outliers, and making informed decisions in data-driven fields.
For those seeking to deepen their understanding of absolute value, advanced topics await exploration.
Complex numbers extend the concept of absolute value to the complex plane, introducing new dimensions and applications.
Inequalities involving absolute value provide intriguing challenges in mathematical problem-solving.
To delve deeper into these topics and gain a comprehensive grasp of absolute value, consider exploring textbooks, academic resources, and online tutorials.
Absolute value measures the distance of a number from zero.
It is represented using vertical bars, like |x|.
Yes, it's always non-negative.
Consider both positive and negative cases: x = 10 and x = -4.
|x + y| ≤ |x| + |y|.
It's used in physics, finance, and data analysis to quantify differences and distances.
It measures distances between points and aids in shape definitions.
They have V-shaped graphs.
MAD quantifies data spread in data analysis.
Yes, complex numbers and inequalities with absolute value are advanced areas of study.



















































































































































