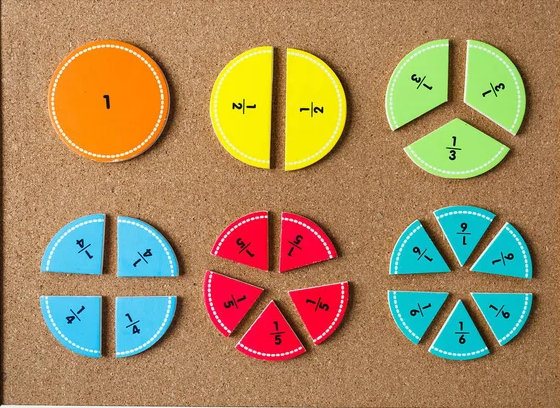



Fractions, foundational in mathematics, express parts of a whole.
The fraction 3/5 embodies the concept; 3 denotes the part we possess, and 5 represents the total parts forming the whole
Essential for advanced math and real-world scenarios, understanding fractions enables precise division and sharing.
Equivalent fractions, like 1/2, 2/4, and 3/6, differ in representation but signify the same quantity.
This foundational concept underpins simplification and comparison, showcasing the versatility of fractions in expressing identical values through diverse numerical combinations.
Discovering equivalent fractions involves strategic multiplication or division of numerators and denominators.
These methods provide alternative representations, essential for varied mathematical operations, fostering numerical flexibility and fluency.
Original Fraction: 3/5
To find an equivalent fraction, let's strategically multiply both the numerator and denominator by the same non-zero number.
Example Calculation:
3/5×2/2
Result: 6/10
In this example, multiplying both the numerator (3) and the denominator (5) by 2 yields the equivalent fraction 6/10.
This demonstrates how strategic multiplication provides an alternative representation of the original fraction, essential for diverse mathematical operations and enhancing numerical flexibility.
Simplification, reducing fractions to their simplest form, relies on dividing both numerator and denominator by their greatest common factor.
Illustrated by 12/18 simplifying to 2/3, this process captures the essence of mathematical precision in representation.
Fraction comparison demands a common denominator, ensuring accurate assessment of magnitudes.
Converting fractions to a shared base, such as finding a common denominator for 3/4 and 5/8, elucidates their relative sizes, a fundamental skill in mathematical analysis.
Essential for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, equivalent fractions streamline operations by requiring a common denominator.
This principle ensures accuracy and coherence in diverse mathematical contexts, strengthening problem-solving capabilities.
Visualization enhances understanding, utilizing models like fraction bars or circles.
Picturing fractions as portions of a whole, such as 1/2 representing half a circle, facilitates grasping how 2/4 and 3/6 portray identical proportions.
Practicality shines in scaling recipes where equivalent fractions permit flexible adjustments while maintaining proportionality.
If a recipe calls for 1/2 cup of flour, knowing 2/4 or 3/6 cups are equivalent ensures accurate adaptations without compromising the recipe's integrity.
Overcoming challenges and mastering equivalent fractions relies on consistent practice.
Exercises like determining the equivalent fraction of 5/8 or simplifying 10/15 reinforce these skills, instilling confidence in handling intricate fraction calculations.
Exercise: Determine the Equivalent Fraction of 5/8
To find an equivalent fraction, you can multiply both the numerator and denominator by the same non-zero number. In this case, let's use multiplication by 2.
5/8x2/2
The result is:
10/16
So, 10/16 is an equivalent fraction to 5/8 obtained by multiplying both the numerator and denominator by 2.
Equivalent fractions represent the same value but have different numerators and denominators. They share a proportional relationship.
Multiply or divide both the numerator and denominator of a fraction by the same non-zero number.
They offer flexibility in mathematical operations and allow for diverse representations of the same quantity.
Sure, 1/2, 2/4, and 3/6 are equivalent fractions, all representing the same half of a whole.
Yes, equivalent fractions represent the same portion of a whole, despite having different numerical representations.
They are utilized in tasks like scaling recipes, adjusting measurements, and understanding proportions in various real-world scenarios.
Yes, any fraction can be considered equivalent to itself when multiplied or divided by 1.
No, equivalent fractions preserve the value of the original fraction; they just offer different numerical expressions.
Common denominators, often achieved through equivalent fractions, are essential for adding and subtracting fractions.
Equivalent fractions aid in simplification by providing alternative representations that can be reduced to their simplest form.



















































































































































